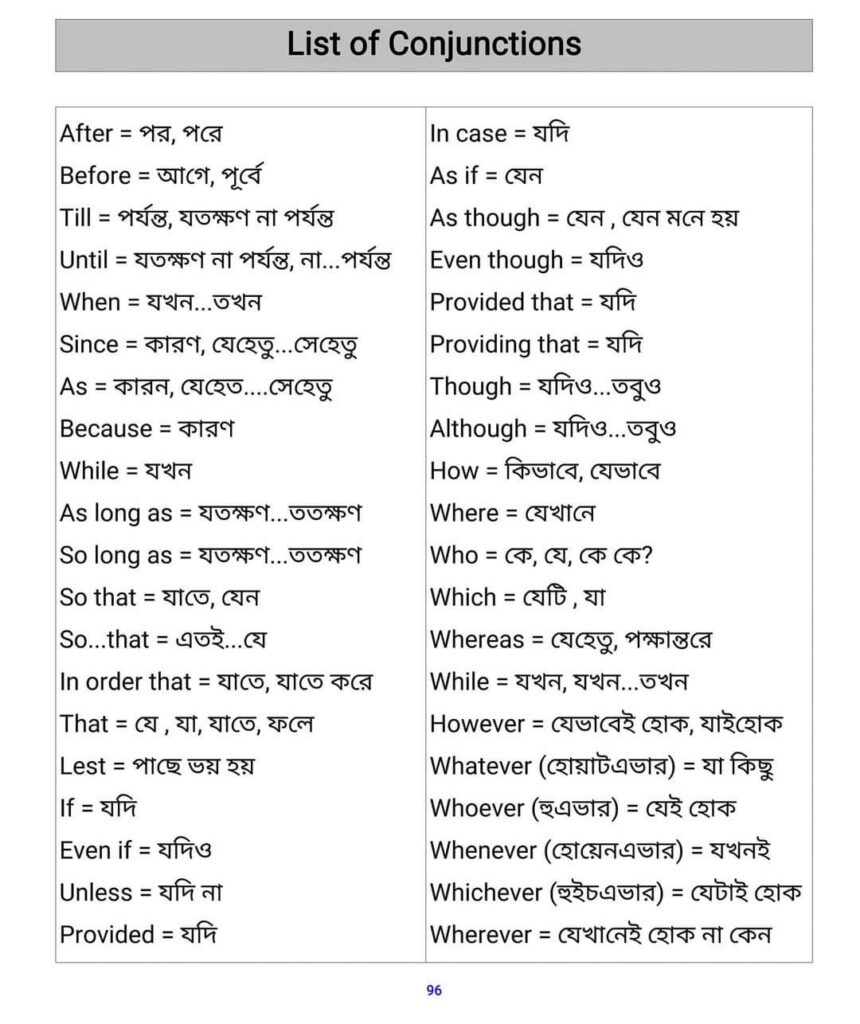
Conjunctions কাকে বলে, কত প্রকার ও Conjunction এর ব্যবহার
Table of Contents
Conjunctions কাকে বলে ও Conjunction এর ব্যবহার
দুই বা দুইয়ের বেশি সমশ্রেণীর word, phrase বা clause যে word যুক্ত করে, তাকে Conjunction বলে।
More Definition of Conjunction
A conjunctions is a word for joining one word to another word, or one sentence to another sentence.
– J.C. Nesfield
A Conjunction is a word used to join words of sentence.
– Wren & Martin
A Conjunction is a joining word of making sentences.
– Dr. Sazzad Hossain
Conjunctions কত প্রকার ও কি কি?
Conjunction তিন প্রকার।
যথাঃ
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Correlative Conjunction
Co-ordinating Conjunctions কাকে বলে?
যে Conjunction দুই বা ততোধিক সমশ্রেনীর word, phrase বা clause কে যোগ করে, তাকে Coordinating Conjunction বলে।
Co-ordinating Conjunctions কত প্রকার?
Co-ordinating Conjunction কে আবার চার ভাগে ভাগ করা হয়েছে।
যথা:
- Cumulative Conjunction
- Adversative Conjunction
- Alternative Conjunction
- Illative Conjunction.
Cumulative Conjunctions কাকে বলে?
যে Conjunction দু’টি সমশ্রেণীর Word বা Clause– কে যুক্ত করে, তাকে Cumulative Conjunction বলে।
যেমন:
- Hasan and Zaman will come today.
Adversative Conjunctions কাকে বলে?
যে Conjunction দ্বারা দুটো বক্তব্যের মাঝে বিপরীত অর্থ বুঝায়, তাকে Adversative Conjunction বলে।
যেমন:
- Hasan is poor but honest.
Alternative Conjunctions কাকে বলে?
যে Conjunction দ্বারা দুটো বক্তব্যের মধ্যে একটিকে বেছে নেওয়া বুঝায়, তাকে Alternative Conjunction বলে।
যেমন:
- Do or die.
Illative Conjunction কাকে বলে?
যে Conjunction যারা কার্যকরণ সম্পর্ক বা অনুমান বুঝায়, তাকে Illative Conjunction বলে।
যেমন:
- We respect him, for his honest.
Subordinating Conjunction কাকে বলে?
যে Conjunction দ্বারা Principal Clause ও Sub-ordinate Clause কে যুক্ত করে, তাকে Sub ordinating Conjunction বলে।
যেমন:
- I saw her while I was walking.
Subordinating Conjunction কত প্রকার?
Subordinating Conjunction কে আবার নয় ভাগে ভাগ করা হয়েছে।
যথাঃ
- Time
- Cause
- Condition
- Purpose
- Comparison
- Manner
- Concession
- Effect
- Apposition
Subordinating Conjunction এর ব্যবহার
Time Cause কি?
face after, when, while. since, as soon as, as till as, till, until, before ইত্যাদি Subordinating Conjunction হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
যেমন:
- Wait here till we come back.
- wait here as long as it rains.
Cause কি?
কারণ নির্দেশ করতে as since. because ইত্যাদি Sub-ordinating Conjunction হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
যেমন:
- He succeeded in life because he worked hard.
- Since he was honest, he does not take bribe.
Condition কি?
শর্ত বুঝাইতে Provided that, provided, whether. unless, if, incase ইত্যাদি Sub-ordinating Conjunction হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
যেমন:
- Unless study hard, you will fail in the examination.
- If you come here, I will be happy.
Purpose কি?
উদ্দেশ্য বুঝাতে in order that, lest. that, so that ইত্যাদি Sub-ordinating Conjunction হিসাবে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
যেমন:
- He works hard so that he can succeed in life.
- Walk fast lest you should miss the train.
Comparison কি?
তুলনা বুঝাতে so…. as, as……….as, than ইত্যাদি Sub-ordinating Conjunction হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
যেমন:
- Karim is taller than Rahim.
- He is as smart as his brother.
Manner কি?
রীতি বা ধরন বুঝাতে as if, as though, as …so ইত্যাদি Sub-ordinating Conjunction হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
যেমন:
- As you so. so you reap.
- He speaks as he likes.
Concession কি?
স্বীকৃতি বা তুরনা বুঝাতে though, although, as, even if, whoever, whatever, however ইত্যাদি Subordinating Conjunction হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
যেমন:
- Though he is old, he works hard.
- Whoever you may be, you will be arrested.
Effect কি?
কোন কাজের ফলাফল বুঝাতে so…..that, Sub-ordinating Conjunction হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
যেমন:
- The man is so week that he cannot work.
- She is so smart that she gets job easily.
Apposition কি?
কারণ বা উদ্দেশ্য বুঝাতে ‘that’ Sub-ordinating Conjunction হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
যেমন:
- We know that he is an honest man.
- The news that the man is dead is false.
Cor-relative Conjunction কাকে বলে?
জোড়ায় জোড়ায় যে Conjunction ব্যবহৃত হয়, তাকে Cor-relative Conjunction বলে।
যেমন:
- As……….as, both……….and, Eihter……….. or etc.
✔️Example of Some Conjunctions
- or (অথবা)
- so-that (এতই যে)
- either-or (হয় এটা না হয় ওটা)
- hardly/scarcely had-when (সঙ্গে সঙ্গেই)
- neither-nor (এটাও না ওটাও না)
- but (কিন্তু)
- so that (যাতে)
- when/ as (যখন)
- not only-but also (শুধু এটাই নয়..ওটাও)
- whom (যাকে)
- since/because/as (যেহেতু)
- before (আগে)
- no sooner had-than (হতে না হতেই)
- till (যতক্ষণ পর্যন্ত)
- as if/as though (যেন)
- until (যতক্সন পর্যন্ত নয়)
- so/therefore (তাই)
- in stead of (পরিবর্তে)
- in spite of (স্বত্বেও)
- such….that (এমন যে)
- and (এবং)
- how (কিভাবে)
- if/provided (যদি)
- though/although (যদিও)
- while (যতক্ষন)
- who (কে)
- whose (যার)
- what (কি)
- after (পরে)
- which (যেটা)
- as soon as (যখনই)
- as well as (এবং)
- where (যেখানে)
- unless (যদি না)
- lest-should (পরে কিছু না ঘটে)
- enough (যথেষ্ট)
- yet (এখনও)
- too… to (এত যে)
✔️More examples in sentence:
- You should lean English—- you can get higher education.
তোমার ইংরেজি শেখা উচিত- তুমি উচ্চ শিক্ষা লাভ করতে পার। এখানে উদ্দেশ্য প্রকাশক দুটি (clause) কে অর্থানুসারে conjunction দ্বারা যুক্ত করা প্রয়োজন। তাই so that in order that (যাতে) বসছে ।
এভাবে অর্থানুসারে নিচেরগুলো করতে হবে
- —–we study hard, we cannot make a good result. (Unless)
- I have a brother—–reads in D.U. (who)
- The thief—– was arrested yesterday has been freed. (who)
- —–he was poor, he became famous. (Though)
- He was poor—– he became famous. (but)
- No sooner had we left the station——the train left. (than)
- He is not only my classmate —–my friend. (but also)
- He is—– an educationalist but also a politician. (not only)
- He is both a poet——a philosopher. (and)
- He is neither my friend —— my classmate. (nor)
- He is so dishonest —– he can deceive me. (that)
- He is so helpful—–he helps everybody. (that)
- I would rather fail—–copy. (than)
- I would—–suffer than take your help. (rather)
- He is working hard—-he should fail. (lest) .
- It is two years —–I met last. (since)
- It is two years —–we had met last. (since)
- Hasan behaves—– he were king (as if)
- Hasan spoke—— he had known it. (as if)