Noun কাকে বলে, কত প্রকার? Noun এর ব্যবহার?
Table of Contents
Noun কাকে বলে কত প্রকার ও কী কী ও Noun এর ব্যবহার?
যে শব্দ দ্বারা কোন ব্যক্তি, বস্তু, স্থান, পদার্থ, দোষ বা কোন গুণের নাম বুঝায়, তাকে Noun বলে।
More Definition of Noun
A Noun is a word used for naming some person or thing.
-J.C. Nesfield
A Noun is a word used as the name of a person, place or thing.
-Wren & Martin
A Noun is a naming word which refers to any person, place and thing.
-Fardeen Islam Saagar
Examples of Noun (বিশেষ্য)
ব্যক্তির নামঃ
- Afzal, Masum, Zaman, Parvez. Imran etc.
স্থানের নামঃ
- Dhaka, Khulna, Sylhet. Rajshahi, Faridpur etc.
প্রানির নামঃ
- Tiger, lion, bird, dove, dog etc.
দেশের নামঃ
- Bangladesh, Iran. India, Pakistan, Japan,
বস্তর নামঃ
- Pen, book, chair, table, fan etc.
পদার্থের নামঃ
- Water, milk. oxygen, iron, oil etc.
গুণের নামঃ
- Honesty, wisdom, beauty, mercy etc.
অবস্থার নামঃ
- Sadness, happiness, wealth, riches, poverty etc.
যেভাবে Noun চেনা যায়
শব্দের শেষে সাধারণত sion, ion. ce, ment, ist, Cour. ty. er, an ইত্যাদি suffix থাকে।
যেমনঃ
- Competence, Decision. Education. Development. Novelist. Patriotism, etc.
Note: মনে রাখবেন, prefix যুক্ত শব্দের ও Parts of speech নির্ণয় করতে suffix -এর মত শব্দের শেষ অংশের উপর নির্ভর করতে হয়।
যেমন:
- dishonesty—— Noun
- dishonest——- Adjective.
উপরের শব্দ দুটিরই শুরুতে dis prefix স্বত্ত্বেও ১মটি Noun, এবং ২য়টি Adjective হয়েছে।
Textual Noun (বিশেষ্য) কি বা কাকে বলে?
*যেখানে Noun বসেঃ
কি বা কিসের অর্থে বাক্যের যেখানেই শব্দ ব্যবহৃত হোক সেটি Noun হবে।
যেমন :
He এখানে তার কি আছে? এই প্রশ্নের উত্তর হিসেবেই কোন শব্দ আনতে হচ্ছে। উত্তর শব্দটি আসতে পারে তার নৈতিকতা (Morality) আছে। এটি একটি শব্দ বা Noun.
✔️A, an. the, that, my, your, his, our its ইত্যাদি Determiner বা নির্দেশকের পরে Noun বসে।
যেমনঃ
- I have not yet taken my decision.
✔️Sentence এর শুরুতে subject হিসাবে Noun (বিশেষ্য) বসে।
যেমনঃ
- Patriotism is a noble virtue.
✔️Verb এর object হিসেবে Noun (বিশেষ্য) বসে।
যেমন:
He took a decision.
✔️Preposition এর পরে Noun (বিশেষ্য) বসে।
যেমন:
- We depend on Allah.
✔️Article এর পর Noun (বিশেষ্য) বসে।
যেমন:
- He is the chairman in our locality.
✔️Adjective এর পর Noun বসে।
যেমনঃ
- Bangladesh is a democratic country.
Examples:
- Illiteracy is one of the greatest problems in Bangladesh
নিরক্ষরতা বাংলাদেশের একটি অন্যতম সমস্যা।
- The definition of education needs to be changed
শিক্ষার সংঙ্গা পবিবর্তন করা প্রয়োজন ।
- Computers have brought a revolution all over the world
কম্পিউটার সারা বিশ্বে বিপ্লব বয়ে এনেছে।
- People don’t find happiness by living separately
মানুষ আলাদাভাবে বাস করে সুখ পায় না।
- Development is not possible without honesty
সততা ছাড়া উন্নয়ন সম্ভব না।
- Happiness depends on mind
সুখ মনের উপর নির্ভর করে।
- Corruption is a great problem in our country
দুর্নীতি আমাদের দেশে বড় সমস্যা।
Noun কত প্রকার ও কী কী?
ইন্দ্রিয়গ্রাহ্যতা হিসাবে Noun প্রধানত দু’প্রকার।
যথাঃ
- Abstract Noun
- Concrete Noun
Abstract Noun কাকে বলে?
যে Noun কোন ব্যক্তি বা বস্তুর অবস্থা, গুণ বা প্রকৃতি সম্পর্কে ধারণা ব্যক্ত করে তাকে Abstract Noun বলে।
Abstract Noun এর বাহ্যিক কোন অস্তিত্ব নেই। একে দেখা বা স্পর্শ করা যায় না। এটি শুধু অনুভূতির সাহায্যে ধারণা করা যায়।
যেমনঃ
- Forgiveness,
- honesty, freedom,
- happiness, childhood.
- friendship,
- education,
- beauty,
- death,
- importance,
- policy.
- love etc.
Example:
He has lost his father in his childhood. ( Abstract Noun)
Now, he is a father of child. (Concrete Noun)
He has shown his heroism. (Abstract noun)
Now, he is a national hero. (Concrete Noun)
Concrete Noun কাকে বলে?
যে সকল Noun এর বাহ্যিক অবস্থান আছে এবং যাকে ইন্দ্রিয়ের দ্বারা অনুভব করা যায়, তাকে Concrete Noun বলে।
যেমন:
- Table. chair. pen. book etc.
Concrete Noun কত প্রকার?
Concrete Noun আবার চার প্রকার।
যথা :
- Proper Noun
- Collective Noun
- Common Noun
- Material Noun.
Proper Noun কাকে বলে?
যে Noun দ্বারা কোন নির্দিষ্ট ব্যক্তি, বস্তু বা স্থানের নাম বুঝায়, তাকে Proper Noun বলে।
যেমনঃ
- Arman is a good boy.
- Khulna is a big city.
- The Padma is a big river.
উপরের Sentence গুলোতে Arman একটি নির্দিষ্ট বালকের নাম, Khulna একটা নির্দিষ্ট জেলার নাম এবং Padma একটি নির্দিষ্ট নদীর নাম সুতরাং এরা প্রত্যেকেই Proper Noun.
Note: Proper Noun এর প্রথম অক্ষর সর্বদাই Capital letter হবে।
যেমন:
- The Meghna is a big river.
✔️নদী, সাগর, মহাসাগর, উপসাগর, দ্বীপপুঞ্জ, সংবাদপত্র, ধর্মগ্রন্থ, মহাকাব্য, পর্বতমালা এ জাতীয় Proper Noun এর পূর্বে The বসে।
যেমন:
- The Padma The Atlantic
- The Bay of Bengal.
- The Daily Star etc.
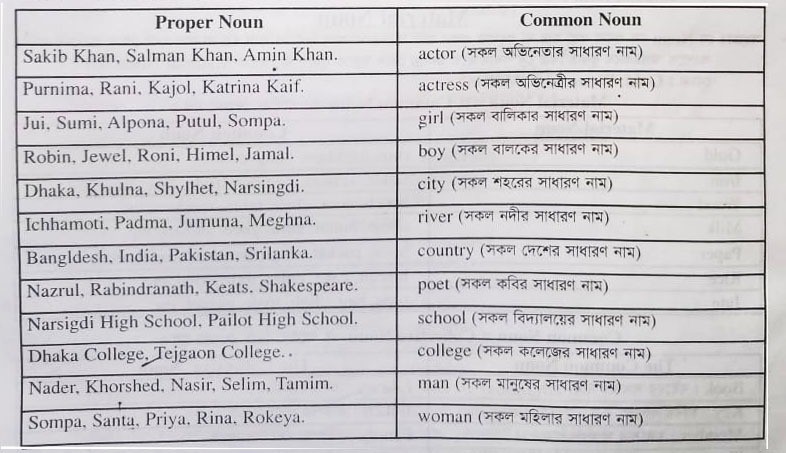
Common Noun কাকে বলে?
যে Noun দ্বারা একই শ্রেণীর ব্যক্তি, বস্তু ল প্রাণীর সাধারণ নাম বুঝায়, তাকে Common Noun বলে।
যেমন:
- Dhaka is a big city.
- Nazrul is a great poet.
- Sakib is a smart boy.
- The Padma is a river.
উপরের Sentence গুলোতে city সকল শহরের সাধারণ নাম হিসেবে, poet সকল কবির সাধারণ নাম হিসেবে, boy সকল বালকের সাধারণ নাম হিসেবে এবং river সকল নদীর সাধারণ নাম হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়েছে। তাই এদেরকে Common Noun বলে।
Note: Common Noun. singular এবং plural উভয় number হয়।
নিচের ছকটিতে Proper Noun এবং Common Noun এর প্রার্থক্য দেখানো হল:
Common Noun এর ব্যবহার
Common Noun কে তিন ভাবে ব্যবহার করা যায়।
✔️বাক্যের প্রথমে The ব্যবহার করে।
যেমনঃ
- The rose is a nice flower.
- The bird flies in the sky.
- The cow is a useful animal.
✔️বাক্যের প্রথমে a/an ব্যবহার করে।
যেমনঃ
- A rose is a nice flower.
- A bird flies in the sky.
- A cow is a useful animal.
- An ant is industrious.
✔️বাক্যের প্রথমে Plural Number ব্যবহার করে।
যেমনঃ
- Roses are nice flowers.
- Birds fly in the sky.
- Cows are useful animals.
Note: Common Noun এর Singular বা Plural উভয় Number হয়।
Collective Noun কাকে বলে?
যে Noun একই জাতীয় কোন ব্যক্তি বা বস্তুকে পৃথকভাবে না বুঝিতে তাদের সমষ্টিকে বুঝায়, তাকে Collective Noun বলে।
যেমনঃ
- Jury, army, class, crowd, gang, flock, audience, committee etc.
Note: Collective noun সর্বদা singular number হয় ।
- The club is going to organize some cultural programmers.
- My family consists of five members
Note: Audience, cattle. clergy, herd, peasantry, police, etc. plural form হিসাবে বিবেচিত করা হয়। এদের কোন singular form নেই।
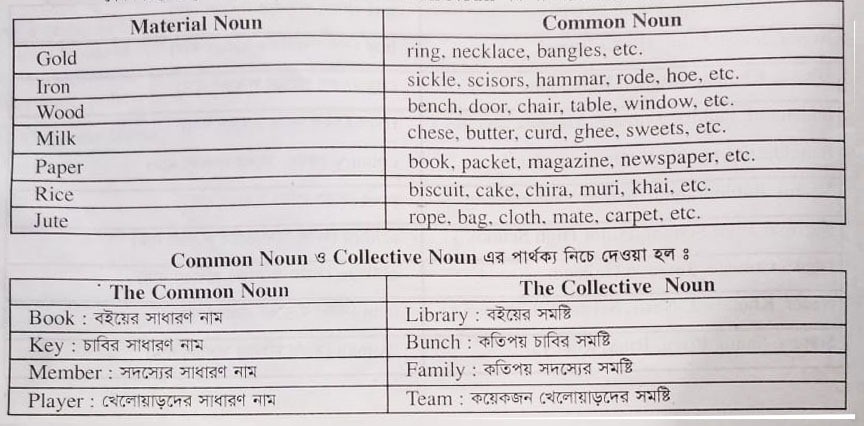
Material Noun কাকে বলে?
যে Noun কে গণনা করা যায় না শুধুমাত্র ওজন দ্বারা যাদের পরিমাণ নির্ধারণ করা হয় বা যার দ্বারা কোন পদার্থের আংশকে অন্যভাবে বুঝায় কিন্তু সে পদার্থ হতে উৎপন্ন কোন বস্তুকে বুঝায় না, তাকে Material Noun বলে।
যেমনঃ
- Gold, Water. Iron. Milk etc.
Material Noun এবং Common Noun এর পার্থক্য দেওয়া হলঃ
Countable and Uncountable Noun
গণনার উপর ভিত্তি করে Noun কে দুই ভাগে ভাগ করা হয়।
যথাঃ
- Countable noun.
- Uncountable noun.
Countable noun কাকে বলে?
Countable noun: যে Noun কে গণনা করা যায়, তাকে Countable noun বলে।
যেমনঃ
- book, pen, table etc.
Countable Noun এর বৈশিষ্ট্য
Countable noun: Singular এবং Plural উভয় Number হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
যেমনঃ
- I have a book.
- I have two books.
✔️Singular countable noun-এর পুর্বে this, that, each, either, neither. a. an, the determiner ব্যবহৃত হয়।
যেমন :
- This is a pen.
✔️অনির্দিষ্টভাবে কোনো ব্যক্তিকে বুঝাতে singular countable noun এর পূর্বে some বসে।
যেমনঃ
- Some boy has come.
Uncountable Noun কাকে বলে?
Uncountable noun: যে Noun গণনা করা যায় না কিন্তু অনুভূতি বা কল্পনার দ্বারা অনুভব করা যায়, তাকে Uncountable noun বলে।
যেমনঃ
- Milk, water, rice, sugar, kindness etc..
Uncountable Noun এর বৈশিষ্ট্য
সাধারণত Uncountable Noun এর পূর্বে Article a/an বসে না।
কিন্তু Uncountable noun এর আগে Adjective ব্যবহৃত হলে সেক্ষেত্রে a/an বসে।
যেমনঃ
- She received a good education.
Note: নিচের Noun গুলো Countable এবং Uncountable উভয় প্রকার Noun হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
Time:
- Don’t waste your valuable time. (uncountable)
- It is a good time for you. (countable)
Work :
- My success was achieved by hard work. (uncountable)
- I have read most of the works of Keats. (countable)
Beauty:
- She is nothing but paragon of beauty. (uncountable)
- The new car is an absolute beauty. (countable)
Justice :
- Hazrat Omar was an embodiment of Justice. (uncountable)
- She was not given a fair Justice. (countable)
Stone :
- The statue is made of stone. (uncountable)
- He threw a stone at me. (countable)
Hair :
- My hair is black. (uncountable)
- He has found a hair in his food. (countable)
Talk :
- Too much talk is very bad. (uncountable)
- I have an important talk with you. (countable)
Danger :
- She is now out of danger. (uncountable)
- Smoking is a danger to health. (countable)
Decision:
- Your decision is not correct. (uncountable)
- Give a decision to the issue. (countable)
Carpet :
- They had a nice carpet in the living-room. (countable)
- We bought ten square meters of carpet. (uncountable)
Glass :
- Could I have a glass of water of water, please? (countable)
- They bought some glass for the window. (uncountable)
নিচে আরো কিছু Uncountable noun উদাহারণ দেওয়া হল
Fluids (তরল পদার্থ):
- water, milk, oil, ink, soup.
Gasses (বায়বীয় পদার্থ):
- hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, air, smoke.
Natural phenomena (প্রাকৃতিক ব্যাপার):
- electricity, heat, darkness, sunshine, weather.
Materials too small to blew counted (গুণা যায় না এমন ক্ষুদ্র ক্ষুদ্র কণাবিশিষ্ট পদার্থ) :
- sand, dirt, salt, rice, flour.
Academic disciplines (পাঠ্য বিষয়):
- mathematics, geography, physics, chemistry, biology.
Abstractions (দেখা বা ধরা-ছোয়া যায় না এমন কিছু):
- love, sympathy, courage, beauty, freedom.
Other intangibles (অন্যান্য অদৃশ্য বিষয়):
- work. advice, information. knowledge.
Diseases (ব্যাধি):
- cholera, malaria, diabetes. influenza, dysentery.
Languages (ভাষা):
- Bengali, English, French, German. Russian.
Games (খেলাধুলা):
- football, cricket, hockey, chess, tennis, golf.
Solid substances (কঠিন বা শক্ত জিনিস বা পদার্থ):
- earth, bread, cotton, nylon.
Verbal nouns (verb থেকে সৃষ্ট noun) :
- camping, cooking, packing, jumping, running.
Noun এর কাজ
✔️*Noun Verb এর Subject হিসেবে কাজ করে।
- Dhaka is the capital of Bangladesh.
- Education is the backbone of a nation.
✔️“Noun Verb এর Object হিসেবে কাজ করে।
- We eat rice.
- We drink water.
✔️ ‘Noun’ Noun এর Adjective হিসেবে কাজ করে।
- He is a school teacher.
- Hasan is a taxi driver.
✔️‘Noun’ Case in Apposition হিসাবে কাজ করে।
- Kazi Nazrul Islam, the rebel poet of Bangla Literature, died in 1976.
- Mr. Aziz, the head teacher of Kurmitola High School, is an honest man.
✔️‘ Noun Preposition এর Object হিসেবে কাজ করে।
- I am fond of flowers.
- He is fond of cricket.
✔️’Noun Object এর Complement হিসেবে কাজ করে।
- We elected him captain.
- We elected him chairman.
✔️‘Noun’ Linking Verb এর Complement হিসাবে কাজ করে।
- He is a student.
- He is a teacher.





